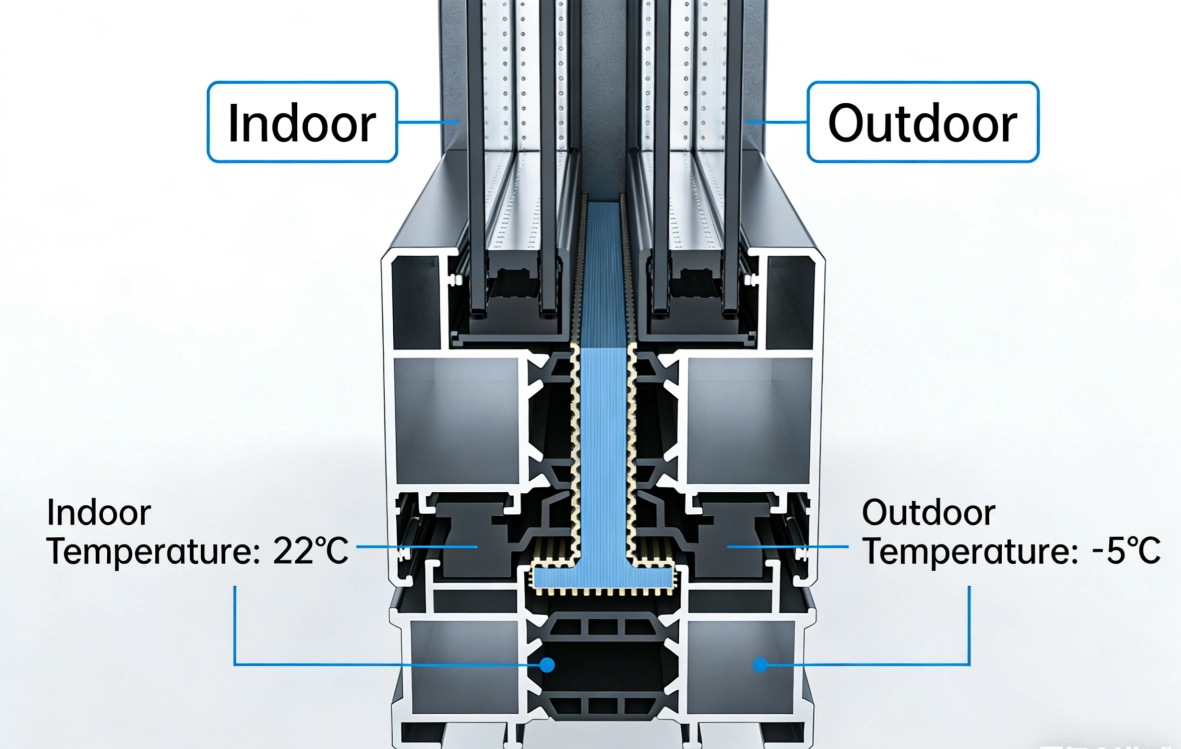
A Thermal Barrier Strip is a critical component used in modern aluminum window, door, and facade systems to reduce heat transfer between the interior and exterior of a building. Aluminum is an excellent structural material, but it is also a very good conductor of heat. Without a thermal break, cold or heat from outside travels directly through the metal frame into the building, leading to energy loss, condensation, and uncomfortable indoor conditions.
A Thermal Barrier Strip is installed between the inner and outer aluminum profiles, physically separating them and interrupting the heat flow path. This process is known as “thermal breaking.” The strip forms a continuous insulating zone inside the frame, which significantly reduces thermal bridging.
In practice, this means:
- Less heat escapes in winter
- Less heat enters in summer
- Indoor temperatures stay more stable
- Heating and cooling systems work more efficiently
The result is better energy performance, improved comfort, and lower operating costs. From an engineering perspective, the Thermal Barrier Strip is not only about insulation—it is about enabling aluminum systems to meet modern building energy standards while maintaining strength, precision, and durability.
What Are Thermal Barriers Made Of?
Most high-performance Thermal Barrier Strips are made from polyamide (nylon) , typically PA66 reinforced with glass fiber . This material choice is not accidental. It is based on a combination of thermal, mechanical, and environmental performance requirements.
Why Nylon (Polyamide)?
Polyamide offers a unique balance of properties that make it ideal for thermal break applications:
| Property | Engineering Benefit |
| Low thermal conductivity | Reduces heat transfer across frames |
| High tensile and flexural strength | Supports structural loads |
| Glass fiber reinforcement | Improves stiffness and dimensional stability |
| Similar thermal expansion to aluminum | Prevents stress and cracking at joints |
| Excellent moisture resistance | Maintains performance in humid environments |
| Heat resistance | Stable under extreme temperature changes |
A Thermal Strut is essentially a load-bearing version of a Thermal Barrier Strip. While both interrupt heat transfer, a Thermal Strut is engineered to handle higher structural demands, such as wind pressure, heavy glass units, and repeated movement in operable windows and doors.
Advantages of Nylon-Based Thermal Barriers
1. Structural Reliability
The reinforced polyamide can carry loads without deforming, ensuring long-term frame integrity.
2. Dimensional Stability
Frames stay aligned even after years of thermal cycling between hot and cold conditions.
3. Durability
Nylon resists aging, UV exposure, and moisture better than many alternative plastics.
4. Energy Efficiency
The insulating core reduces HVAC demand and improves overall building performance.
From a materials engineering standpoint, nylon-based Thermal Barrier Strip and Thermal Strut systems enable aluminum to behave like an energy-efficient material without sacrificing strength.
How Thermal Barrier Strips Improve Everyday Life
The relationship between Thermal Barrier Strips and daily life becomes most visible at doors and windows. These are the weakest points in the building envelope when it comes to heat loss, air leakage, and condensation.
1. Improved Indoor Comfort
Without a thermal break, aluminum frames become cold to the touch in winter and hot in summer. This creates temperature imbalance near windows and doors, leading to drafts and discomfort.
With a Thermal Barrier Strip in place:
- Inner frame surfaces stay closer to room temperature
- Cold spots near windows are reduced
- Occupants experience fewer drafts
- Living spaces feel more consistent and comfortable
This directly improves how people experience their homes, offices, and public spaces.
2. Reduced Condensation and Moisture Problems
When warm indoor air contacts a cold aluminum frame, condensation forms. Over time, this moisture can:
- Damage finishes
- Promote mold growth
- Affect indoor air quality
Thermal Strut systems keep the interior frame warmer, which reduces the risk of condensation. From a building health perspective, this is a major advantage.
3. Energy Savings and Sustainability
Doors and windows with Thermal Barrier Strips reduce heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. This lowers the load on heating and cooling systems.
Practical results include:
- Lower energy bills
- Smaller HVAC system requirements
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Improved building efficiency ratings
For modern construction, this is not just a comfort issue—it is a regulatory and environmental requirement.
4. Better Acoustic and Weather Performance
Although the primary function is thermal, a properly designed Thermal Barrier Strip also helps:
- Improve air tightness
- Reduce vibration transmission
- Enhance sound insulation
- Increase resistance to wind and rain
This contributes to quieter, more weather-resistant interiors, especially in urban or coastal environments.
Thermal Barrier Strip vs Thermal Strut: How They Work Together
While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there is a functional distinction:
| Term | Main Role |
| Thermal Barrier Strip | Breaks heat transfer and insulates |
| Thermal Strut | Breaks heat transfer and carries structural load |
In advanced window and door systems, both are often integrated into the frame design. The Thermal Barrier Strip ensures insulation, while the Thermal Strut ensures the system can handle pressure, weight, and movement.
Together, they enable aluminum systems to meet modern demands for:
- Energy efficiency
- Structural safety
- Durability
- Long-term performance
Why Thermal Barriers Matter in Modern Building Design
From an engineering perspective, the Thermal Barrier Strip and Thermal Strut are no longer optional features—they are essential components of high-performance building envelopes.
They allow architects and builders to:
- Use aluminum without compromising energy performance
- Meet building codes and efficiency standards
- Improve occupant comfort and health
- Extend the service life of doors and windows
In everyday life, people may not see the Thermal Barrier Strip, but they feel its impact through warmer rooms, quieter interiors, and lower energy costs.
A building’s performance is only as strong as its weakest connection point. Doors and windows are those points—and the Thermal Barrier Strip and Thermal Strut are what turn them from energy liabilities into energy assets. By combining nylon-based materials with precise engineering, these components quietly improve how buildings function and how people live inside them.
Related Articles
How Thermal Break Strips Prevent Heat Transfer in Aluminum Systems?
Are Thermally Broken Windows Worth It?
Structural Advantages of Nylon Thermal Barrier Strips Beyond Insulation?